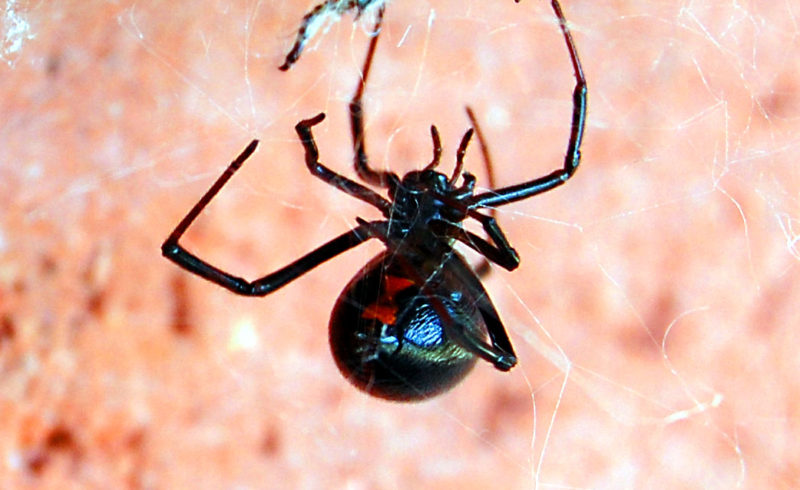
It’s happened again in my daughter’s basement bedroom! A new visitor appeared last week – and this time I became worried too. As she went in to get ready for bed, she flicked on the light, and found a black widow crawling up the wall!
We’ve seen enough black widows outside over the years to know what they look like. Females have shiny black bodies with large abdomens. If you can see the underside of the abdomen, you’ll spot a red hourglass shape or two separate red spots on the underside of the abdomen. We saw the hourglass, so after we got it out of the house, I went online to find out just how dangerous they are.
A Shy Spider
Black widow spiders are actually non-aggressive. They are after prey, not people. They are solitary, shy spiders that are usually content just to hang in their webs. If disturbed, they will retreat to a corner of their webs. They prefer natural dark, quiet, undisturbed areas such as rocks, wood piles, leaf litter, or other debris. But they may come indoors to escape cold weather or drought. Places you can find them include barns, garages, crawl spaces, cellars, and sheds.
The Venom
Only the female black widows bites. The bites usually occur when the spider gets trapped against human skin. A black widow’s bite is said to be 15 times more toxic than that of the prairie rattlesnake. However, when a black widow bites, only a minute amount of toxin is injected. The bites are rarely fatal.
When a person is bitten, a neurotoxin from the spider’s saliva is released into the bloodstream. It can cause a dull pain and severe muscle cramps that may be accompanied by sweating and vomiting. The pain usually peaks after 2 – 3 hours and subsides within 12 to 24 hours. While small children under 30 pounds are the most at risk, anyone who has been bitten should seek medical help immediately.
With more understanding about black widows, both my daughter and I were beginning to feel a little better about the situation. She did spend the next week sleeping upstairs, however.
More Facts about Black Widows
- Female spiders do not always eat the male after mating. This was mostly observed in laboratory conditions when the male had nowhere to go. However, the male may stay around to feed on prey captured by the female.
- The female will act aggressively if she is protecting an egg sac.
- The black widow’s web is strong enough to catch animals as large as mice. The web threads are also used as crosshairs in rifle sights.
- Other prey includes mosquitoes, flies, grasshoppers, caterpillars, and beetles.
To Learn More
Click on one of the links below for more information about black widow spiders.
“The Black Widow.” Alabama Cooperative Extension System.
“Black Widow Spiders.” National Geographic.
“Southern and Northern Black Widow Spiders.” University of Arkansas.
Photo by cohdra